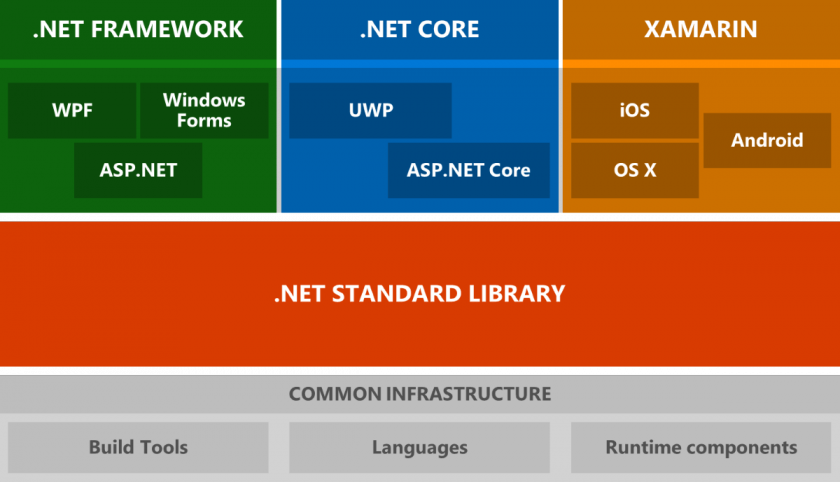
Share code among mobile platforms
One of the biggest advantages of using Xamarin is that it enables code sharing among all three platforms (Xamarin, Windows, and iOS). The source code for applications is written in .NET C# and there is a lot of common code. Examples? The code responsible for connecting with a back-end or data model. The average amount of code sharing can be as high as 70 percent.
Native performance and look
Mobile applications created with Xamarin are truly native mobile applications. They are compiled to native bytecode on each platform and there is no decrease in performance.
The user interface has a native look on each platform, so you can’t distinguish a UI created with Xamarin from one created with a tool dedicated to the each platform (like Xcode or Android Studio).
Link native libraries
Java for Android. Objective-C for iOS. We all know they exist but there is no equivalent provided for Xamarin.
With Xamarin, native libraries can be easily linked, so developers are able to use them all and not have to worry about incompatibility.
Azure: one last piece
Cloud – for sure you’ve heard this word somewhere. But what does it mean, exactly?
Imagine that you want to create an online shop with both web and mobile applications for shopping, and add a database for users and products on top of it. Before you start development, you ask yourself these two questions:
- What is the best architecture for my solution?
- Where will I host all these services?
The cloud is the solution for both issues. You don’t have to buy any hardware, install servers software, or configure everything from scratch. Microsoft Azure (which is our cloud platform of choice) can be helpful here.
Pre-made components for developers (and a bit about security)
Let’s get back to the online shop example. For sure some back-end is needed here and also some type of database to store information. The Azure cloud platform provides pre-made components we can use for these tasks, such as:
- Web apps. Component for the back-end. Source code can be written either in .NET or in JavaScript.
- Databases. You can choose how you would like to store data from your application. It can be either a relational database or not (no-SQL).
- Notifications Hub. A component that sends push notifications to mobile applications. You use it to easily inform users about an added functionality or other product-related news.
Connections between different components hosted on Azure (like the back-end and database) are always encrypted. Azure also provides HTTP certificates by default to secure the connection between a mobile application and the back-end.
Also, Azure provides 24-hour threat management protection of hosted resources, helping to guard against malware and other threats. Which brings us to…
Scalability and Service Level Agreement (SLA)
One of the most important advantages of using Azure is scalability. When the database is full there is an option to enlarge it in just a few steps. The same can be said for web applications capacity. Of course, either of those actions will bump the pricing up a bit.
You can estimate costs with the dedicated Azure calculator.
.NET, Xamarin, and Azure combined
.NET, Azure and Xamarin – what do they have in common?
Back-end, web, and mobile applications can be written with .NET C# and Visual Studio. Azure provides full support for .NET applications.
- Code sharing between projects
Some parts of the source code can be re-used. One example is the data model between mobile applications and back-end.
- Push notifications for mobile applications
With Azure Notification Hub, developers are able to add functionality to inform users with direct notifications coming from the back-end.
- Authentication services available on Azure
Developers can easily integrate social media logins within their back-end and their mobile applications.
- DevOps for mobile applications
With Xamarin, Azure, Test Cloud, and Visual Studio Team Services, you can setup continuous integration to provide applications much faster.
Azure provides databases that can be integrated with back-end and .NET libraries to make mobile data synchronization easier between backend and application.
That’s it!
Thanks for your attention. I encourage you to try out both Azure and Xamarin even if you’re new to .NET. The experience will give you a much broader idea of what the two technologies are about.